Petroleum bitumens are produced in two ways: Straight Run and Air Blowing. The aeration method is used when the bitumen (feed) does not meet the expected properties. In this case, blowing air into the feed (feed) produces a product with modified properties at temperatures between -10º-190ºC. This process is sometimes referred to as Asphalt Oxidation and its product is Oxidized Asphalt, but the terms Air Blowing and Air Blowing Asphalt are more appropriate because of the process of dehydration and polymerization. And oxygen will not enter the aeration product except in very small amounts. In the aeration industry there are two ways of continuous (Batch Process) and continuous (Batch Process).
Bitumen chemistry
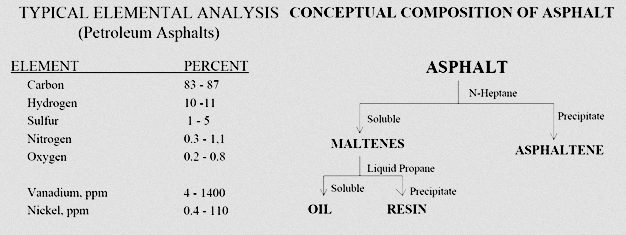
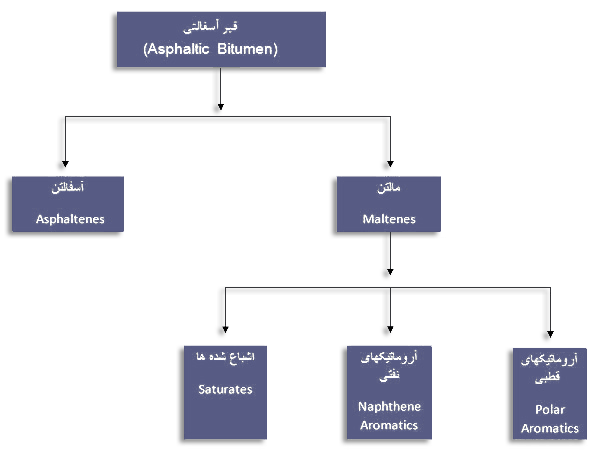
Bitumen; A dark brown-black hydrocarbon compound in solid, semipermeable or viscose form, with a natural or refined origin, containing mainly high molecular weight hydrocarbons. It is completely soluble in carbon disulfide (CS2), trichloroethylene (C2HCl3) and xylene (C6H4 (CH3) 2). Its vapor pressure is negligible at ambient temperature and is almost odorless. The most common and widely used bitumen is petroleum bitumen which is physically a homogeneous material and chemically a heterogeneous mixture of different chemical compositions. This hydrocarbon mixture generally comprises 90% carbon and hydrogen atoms and the rest, nitrogen, sulfur and oxygen, and small amounts of nickel, iron, magnesium, and so on. It has an elastic, not a viscous material, but the bitumen behavior involves a combination of the two viscoelastic
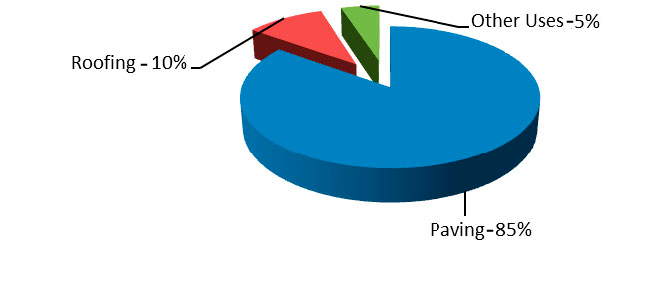
Applications of bitumen
Bitumen is usually used in both construction and insulation areas. Approximately 2% of bitumen is used in road construction, and insulation accounts for only 2% of bitumen consumption, including floor coverings, roofing, underground pipes, metal shielding as well as sealing of tanks, canals, Bridges and fixing of smooth sand, coloring and …
Bitumen Types
Bitumen: A set of bitumens that are naturally produced by the effects of weather and time and are used without the need for distillation methods and are very diverse in composition and properties.
Bitumen Bitumen: Black and hard materials that are remnants of coal tar distillation. Freshly fractured surface is glossy, melts with rapid drop in viscosity during heating and their melting temperature depends on the production method.
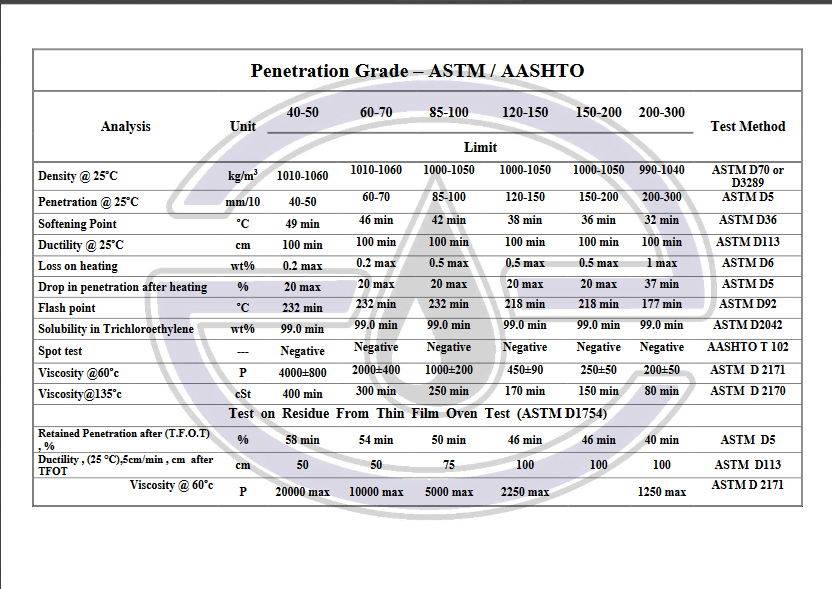
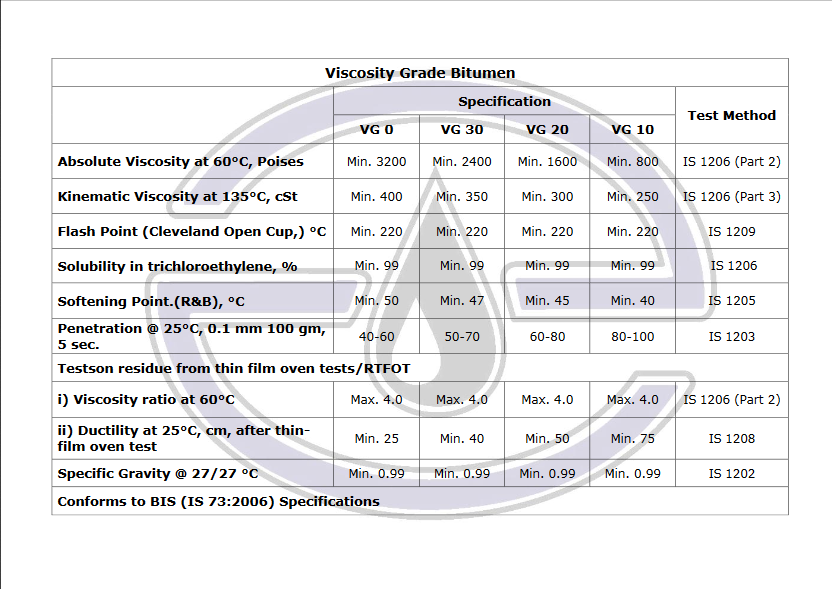
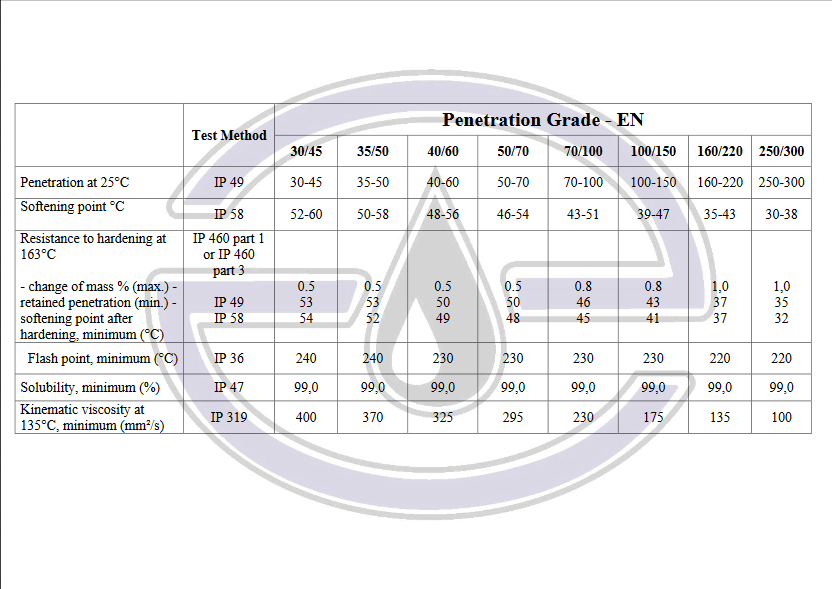
Petroleum bitumen: These are those bitumen whose origin is crude oil. These bitumens are solid and semi-solid bitumens that are obtained directly from the distillation of crude oil or by other additional operations such as blowing air and have higher uses and consumption than other types of bitumen.
Blown Bitumen
Blown bitumen are produced in a vacuum reaction (VB) and air reaction process in bitumen reactors and are produced in different grades depending on the process conditions.
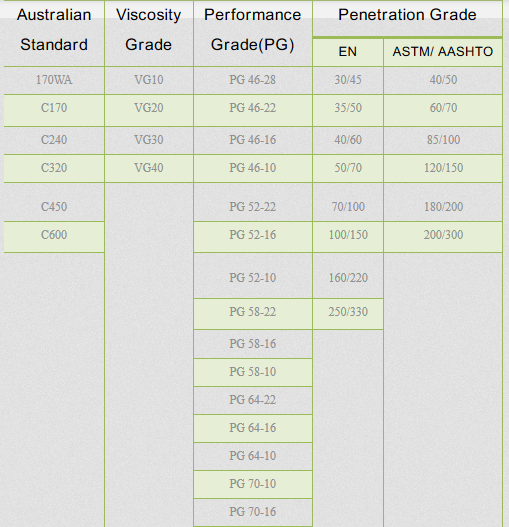
Special bitumen
These types of bitumen are manufactured according to customer requirements with specific specifications for regional and occasional applications and are mainly in the form of modified bitumen and oxidized bitumen.
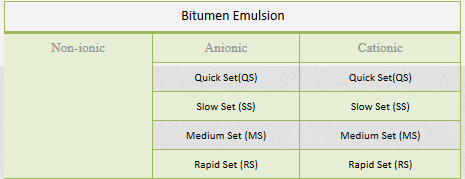
Emulsion bitumen
It is produced by mixing bitumen and aqueous phase for various purposes such as single coat, prime coat, cold asphalt and asphalt restoration, which is divided into three categories: cationic, anionic and neutral depending on the type of stone material. The two-phase mixing speed is classified into four groups: accelerator, accelerator, decelerator, and decelerator. This product complies with environmental requirements and is a good substitute for bitumen
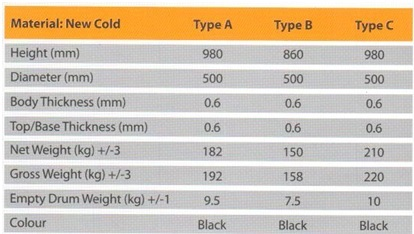
Barrels and overlays
The barrel factory is equipped with production line and automatic color line in accordance with current standards. The 6,000-barrel-a-day plant can produce metal barrels in three different types.
Bitumen packaging in polymer bags has provided the possibility of delivering one tonne of bitumen at a capacity of 30 tons per hour.
The company has 3 full-barrel arms with a capacity of 1,000 tons per day to deliver bitumen to the metal barrel.